MySQL¶
This chapter contains an example of a basic Fudo PAM configuration, to monitor SQL queries to a remote MySQL database server.
In this scenario, the user connects to a MySQL database using individual login and password. When establishing the connection with the remote server, Fudo PAM substitutes the login and the password with the previously defined values: root/password (authorization modes are described in the User authorization modes section).

Prerequisites¶
The following description assumes that the system has been already initiated. For more information on the initiation procedure refer to the System initiation topic.
Configuration¶

Adding a server
is a definition of the IT infrastructure resource, which can be accessed over one of the specified protocols.
- Select > .
- Click .
- Provide essential configuration parameters:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| General | |
| Name | mysql_server |
| Blocked |  |
| Protocol | MySQL |
| Description |  |
| Permissions | |
| Granted users |  |
| Destination host | |
| Address | 10.0.1.35 |
| Port | 3306 |
| Bind address | Any |
- Click .
Adding a user
User defines a subject entitled to connect to servers within monitored IT infrastructure. Detailed object definition (i.e. unique login and domain combination, full name, email address etc.) enables precise accountability of user actions when login and password are substituted with a shared account login credentials.
- Select > .
- Click .
- Provide essential user information:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| General | |
| Login | john_smith |
| Fudo domain |  |
| Blocked |  |
| Account validity | Indefinite |
| Role | user |
| Preferred language | English |
| Safes |  |
| Full name | John Smith |
john@smith.com |
|
| Organization |  |
| Phone |  |
| AD Domain |  |
| LDAP Base |  |
| Permissions | |
| Granted users |  |
| Authentication | |
| Authentication failures |  |
| Enforce static password complexity |  |
| Type | Password |
| Password | john |
| Repeat password | john |
- Click .
Adding a listener
determines server connection mode (proxy, gateway, transparent, bastion) as well as its specifics.
- Select > .
- Click .
- Provide essential configuration parameters:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| General | |
| Name | mysql_listener |
| Blocked |  |
| Protocol | Mysql |
| Permissions | |
| Granted users |  |
| Connection | |
| Mode | proxy |
| Local address | 10.0.150.151 |
| Port | 3306 |
- Click .
Adding an account
defines the privileged account existing on the monitored server. It specifies the actual login credentials, user authentication mode: anonymous (without user authentication), regular (with login credentials substitution) or forward (with login and password forwarding); password changing policy as well as the password changer itself.
- Select > .
- Click .
- Provide essential configuration parameters:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| General | |
| Name | admin_mysql_server |
| Blocked |  |
| Type | regular |
| Session recording | all |
| OCR sessions |  |
| Delete session data after | 61 days |
| Permissions | |
| Granted users |  |
| Server | |
| Server | mysql_server |
| Credentials | |
| Domain |  |
| Login | root |
| Replace secret with | with password |
| Password | password |
| Repeat password | password |
| Password change policy | Static, without restrictions |
| Password changer | |
| Password changer | None |
| Privileged user |  |
| Privileged user password |  |
- Click .
Defining a safe
directly regulates user access to monitored servers. It specifies available protocols’ features, policies and other details concerning users and servers relations.
- Select > .
- Click .
- Provide essential configuration parameters:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| General | |
| Name | mysql_safe |
| Blocked |  |
| Login reason |  |
| Notifications |  |
| Policies |  |
| Users | john_smith |
| Protocol functionality | |
| RDP |  |
| SSH |  |
| VNC |  |
| Accounts | |
admin_mysql_server |
mysql_listener |
- Click .
Establishing connection with a MySQL database¶
- Launch a command line interface client.
- Enter
mysql -h 10.0.150.151 -u john_smith -p, to connect to the database server. - Enter the user’s password.

- Continue browsing the database contents using SQL queries.
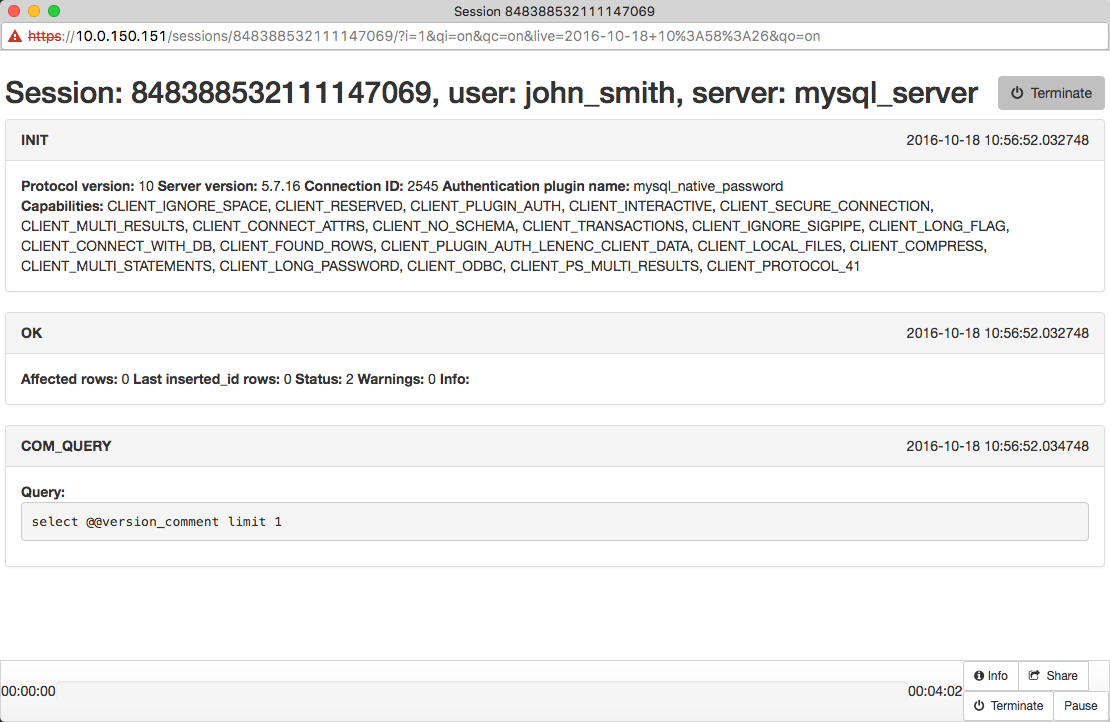
Viewing user session¶
- Open a web browser and go to the Fudo PAM administration page.
- Enter user login and password to log in to Fudo PAM administration panel.
- Select > .
- Find John Smith’s session and click i.

Related topics: