Connection modes¶
Transparent
In transparent mode, users connect to destination server using given server’s IP address.
Gateway
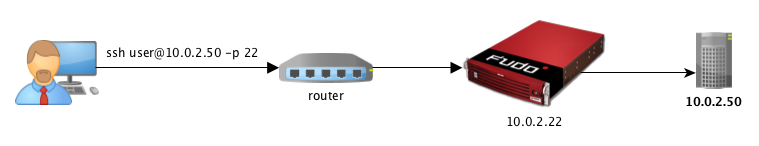
In gateway mode, users connect to destination server using the server’s actual IP address. Fudo PAM mediates connection with the server using own IP address. This ensures that the traffic from the server to the user goes through Fudo PAM.
Proxy
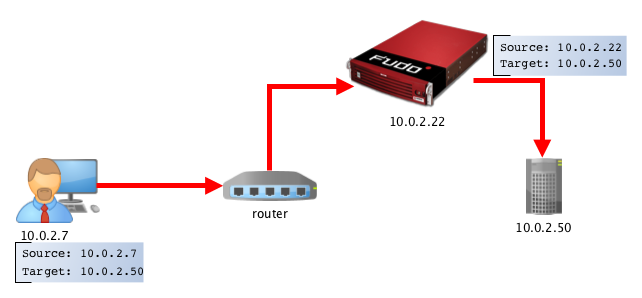
In proxy mode, administrator connects to destination server using combination of Fudo PAM IP address and unique port number assigned to given server. Uniqueness of this combination enables establishing connection with a particular resource.
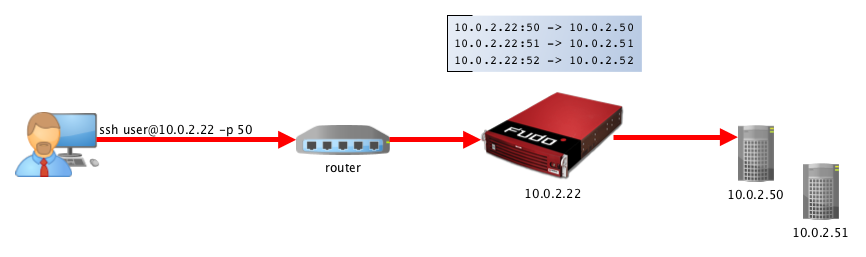
Such approach enables concealing actual IP addressing and allows configuring servers to only accept requests sent from Fudo PAM.
Bastion
Note
The bastion mode is supported when connecting over SSH, RDP, VNC, Telnet, Telnet 3270, Telnet 5250, MS SQL and ICA protocols.
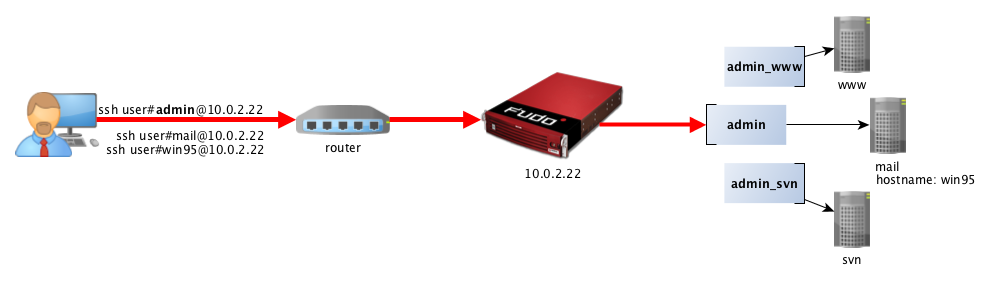
In bastion mode, the account on the target host, or the host itself, is specified within the string identifying the user, e.g. ssh john_smith#admin@10.0.2.22. This enables facilitating access to a group of monitored servers through the same IP address and port number combination.
Note
The string specifying the target object must unambiguously identify an account or a server.
Target object string is matched in the following sequence:
- Exact account name - Fudo PAM tries to match the string with the account object.
- Exact server name - Fudo PAM tries to match the string with the name of a server object.
- Exact server address - Fudo PAM tries to match the string with an IP address of a server object defined in the local database.
- IP address returned by the DNS service - Fudo PAM queries the DNS service and tries to match the returned IP address with an IP address of a server object defined in the local database.
- Hostname returned by the reverse DNS service - Fudo PAM queries the reverse DNS service and tries to match the returned hostname with a sever object defined in the local database.
Note
Due to special interpretation of the \ character by different system shells (e.g. bash), user login and domain combination require specific formatting:
- “domain\user”#bsd01@10.0.60.138
- ‘domain\user’#bsd01@10.0.60.138
- domain\user#bsd01@10.0.60.138
Related topics: